Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources: Vitamin E, a group of eight fat-soluble compounds with alpha-tocopherol as the most biologically active form, plays a pivotal role in sustaining health. In this comprehensive exploration by Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources, we delve into the significance of Vitamin E in our daily diet, its diverse health advantages, and the optimal nutritional sources to ensure ample intake.
The Role of Vitamin E:
Vitamin E primarily acts as an antioxidant, comprising eight fat-soluble compounds with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active. Its function is to neutralize free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage cell structures, contributing to chronic diseases and aging.
Health Benefits of Vitamin E:
- Antioxidant Protection: Vitamin E neutralizes free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and safeguarding cell membranes, preventing chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer, and promoting overall health.
- Heart Health: Vitamin E may lower the risk of heart disease by inhibiting the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, potentially reducing arterial plaque formation. Additionally, it might improve blood vessel function and mitigate inflammation, supporting cardiovascular health.
- Immune System Support: Enhancing immune cell function and shielding them from oxidative damage, Vitamin E supports a robust immune system, aiding the body in effectively combating infections and diseases.
- Skin Health: Vitamin E is vital for healthy skin, protecting against oxidative stress from UV radiation and environmental pollutants, reducing inflammation, and aiding in skin healing. Topical application may enhance skin hydration and elasticity.
- Eye Health: Vitamin E’s antioxidant properties may lower the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss in older adults, preserving overall eye health.
Also Read : Wellhealthorganic.com know the causes of white hair and easy ways to prevent it naturally
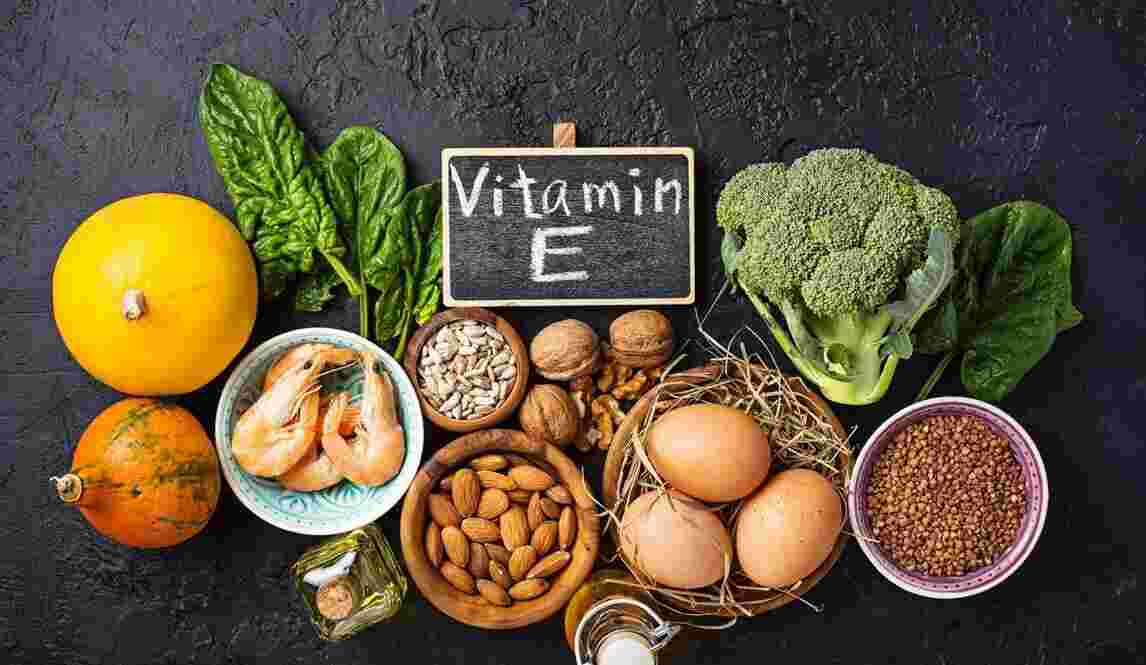
Nutritional Sources of Vitamin E:
To ensure sufficient Vitamin E intake, incorporate a variety of rich foods into your diet:
- Vegetable Oils: Sunflower, safflower, and wheat germ oils are rich in Vitamin E. Olive and canola oils also provide significant nutrients.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, hazelnuts, peanuts, and sunflower seeds are excellent sources. A small daily handful can boost Vitamin E intake.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are Vitamin E-rich. Including these vegetables in meals contributes to a well-rounded, healthy diet.
- Fruits: Avocado and kiwi are Vitamin E sources. Including a variety of fruits ensures meeting daily requirements.
- Fortified Foods: Check nutrition labels for fortified cereals, margarine, and processed foods with added Vitamin E.
- Fish: Salmon, trout, and mackerel contain moderate Vitamin E amounts, along with other essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids.
- Whole Grains: Whole wheat, brown rice, and quinoa offer small amounts of Vitamin E, contributing to overall intake with essential fiber and nutrients.
Also Read : Wellhealthorganic.com know why not to reuse plastic water bottles know its reason in Hindi
Conclusion:
Understanding the importance of Vitamin E and its myriad health benefits is crucial for overall well-being. Informed dietary choices that include a diverse range of Vitamin E-rich foods support a healthier lifestyle. Explore further on Wellhealthorganic.com:vitamin-e-health-benefits-and-nutritional-sources for in-depth insights into Vitamin E and its contributions to health and wellness.
FAQs
1. Why is Vitamin E important for our health?
Ans: Vitamin E is crucial as it acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from free radical damage. It supports heart health, boosts the immune system, maintains skin health, and contributes to eye health.
2. What are the best food sources of Vitamin E?
Ans: Excellent sources of Vitamin E include vegetable oils (sunflower, safflower), nuts and seeds (almonds, hazelnuts), green leafy vegetables (spinach, kale), fruits (avocado, kiwi), fortified foods, and certain types of fish (salmon, trout).
3. How does Vitamin E benefit the skin?
Ans: Vitamin E plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin by protecting it from oxidative stress caused by UV radiation and environmental pollutants. It reduces inflammation, promotes healing, and enhances skin hydration and elasticity.
4. Can Vitamin E reduce the risk of heart disease?
Ans: Yes, Vitamin E may lower the risk of heart disease by preventing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, which can contribute to the formation of arterial plaques. It also improves blood vessel function and reduces inflammation, supporting overall cardiovascular health.
5. Is Vitamin E supplementation necessary, or can it be obtained through diet alone?
Ans: In most cases, a well-balanced diet that includes Vitamin E-rich foods is sufficient to meet the body’s requirements. However, supplementation may be recommended for individuals with specific health conditions or those at risk of Vitamin E deficiency. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking supplements.